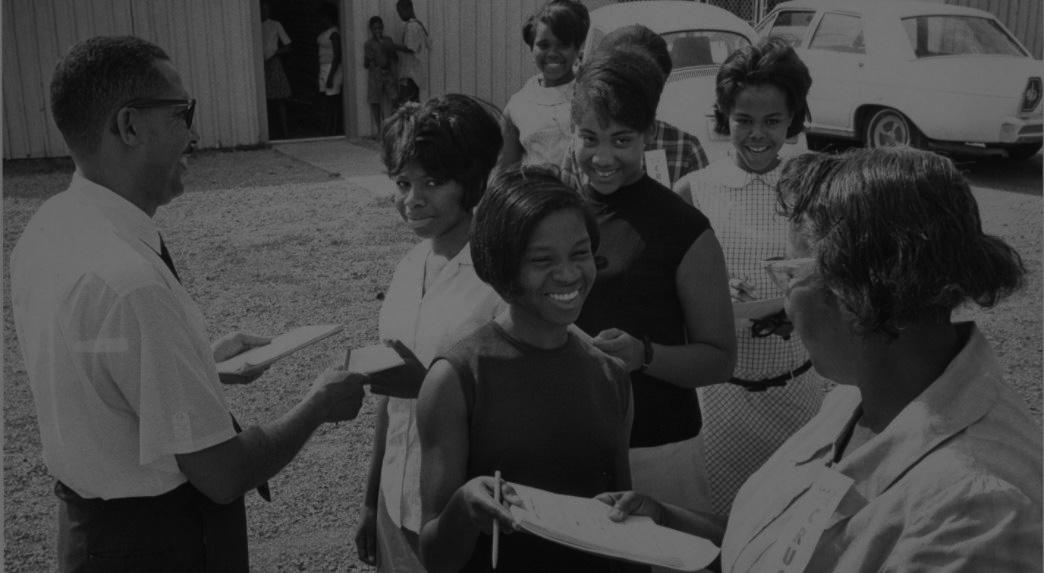
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records
Voter Education Project Organizational Records