Voter Education Project Organizational Records
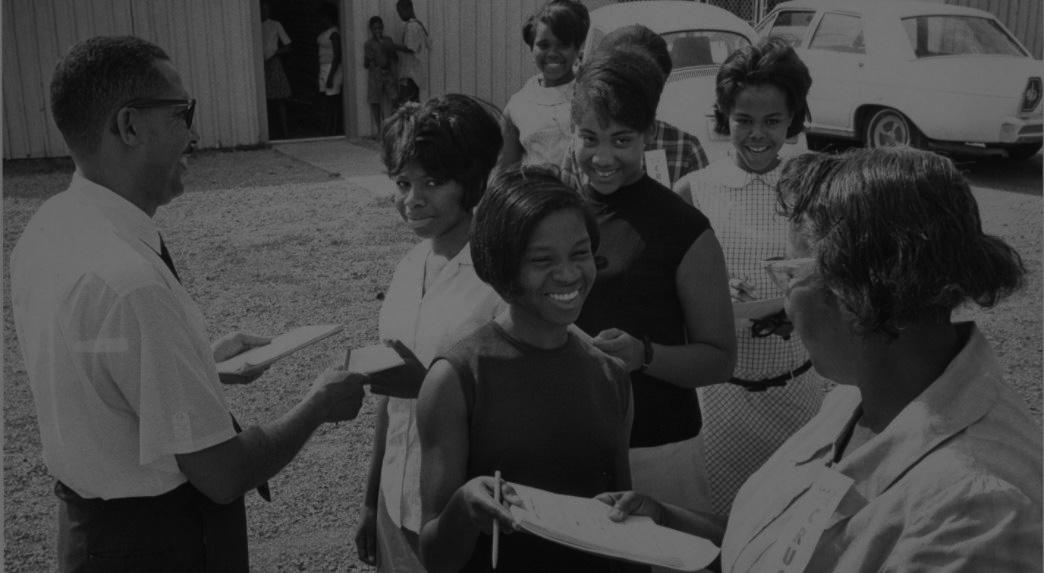
The Voter Education Project (VEP) began in 1962 as part of the Southern Regional Council. Initially VEP granted funds to civil rights organizations to support voter education, voter registration drives, and voting-related research. In 1964, Vernon Jordan, the second executive director of the VEP, expanded the programs goals to include citizenship training, voter education, and leadership training in the southern United States, while continuing to provide funds to independent voter and civil rights groups, including the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC), the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC), and the League of Women Voters. The VEP’s work with the League of Women Voters is highlighted in the materials below. In 1971, VEP under the leadership of John Lewis, became an independent organization and functioned as a research center and became known as an authoritative source for statistics on southern elections and voter registration in general. Lewis also forged the VEP into an activist organization, launching Voter Mobilization Tours with Georgia state legislator and civil rights advocate Julian Bond.
At the AUC Robert W. Woodruff Library we are always striving to improve our digital collections. We welcome additional information about people, places, or events depicted in any of the works in this collection. To submit information, please contact us at DSD@auctr.edu.